Realsense2 Camera
The robot is equipped with an Intel RealSense D435 camera, which can obtain RGB and depth images. The realsense_ros package is a ROS functionality package provided by Intel for calling the D435 camera.。
Starting the Camera
Package Location
/home/lemon/robot_ros_application/catkin_ws/src/realsense/realsense2_cameraLaunch File Path
/home/lemon/robot_ros_application/catkin_ws/src/realsense/realsense2_camera/launch/RobanD435camera.launchStarting the Camera with the Launch File
Due to the mechanism of ROS, nodes with the same name can affect communication, so only one node with the same name can exist. Since the robot automatically starts all functional nodes, including the depth camera node, upon normal startup, you should ensure that the depth camera node started at boot is closed when running the above launch file.
# To close the depth camera node
rosnode kill /camera/realsense2_camera_managerStarting the Depth Camera Node
source ~/robot_ros_application/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
roslaunch realsense2_camera RobanD435camera.launchIf the following error occurs, it indicates that the depth camera node was started repeatedly, causing an abnormal startup.
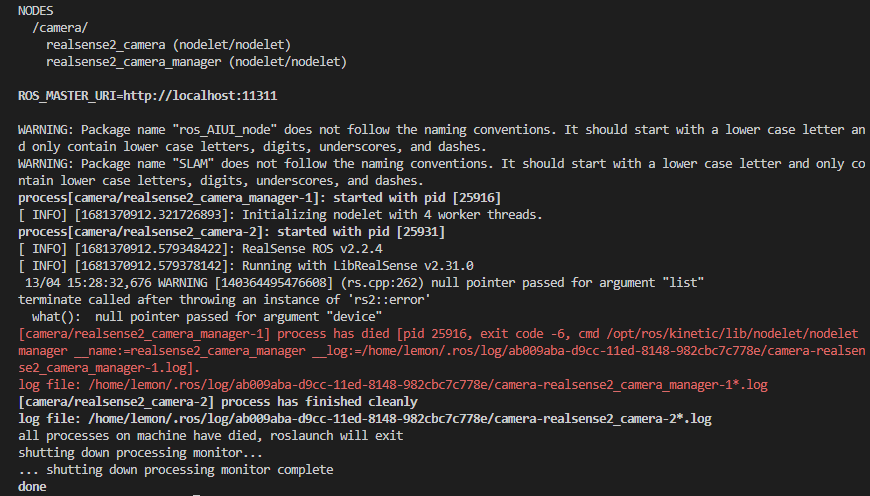
Node Output Topics
The main topics published by the node are:
Camera intrinsic parameters
/camera/color/camera_infoRGB image information
/camera/color/image_rawUnaligned depth information
/camera/depth/image_rect_rawDepth information aligned with RGB images
/camera/aligned_depth_to_color/image_rawThis topic is only output if the
align_depthparameter is set totruein the launch file.
Subscribing to RGB Images
Python Example
#! /usr/bin/env python
# coding=UTF-8
import rospy # ROS Python library
from cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeError # Library for converting msg data type images to OpenCV image format
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image # Message type for the topic
import cv2 # OpenCV-Python library
import numpy as np
class Vision():
def __init__(self):
self.topic_name = '/camera/color/image_raw' # Topic name
self.__cv_bridge = CvBridge()
rospy.Subscriber(self.topic_name, Image, self.__image_callback, queue_size=1) # Define the subscriber, including topic name, message type, callback function, and queue size
def __image_callback(self, msg): # Callback function for the message, the received message is in msg
try:
image_origin = self.__cv_bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, msg.encoding) # Convert to numpy matrix format through cv_bridge
except CvBridgeError as err:
rospy.logerr(err)
return
print("image shape is {}".format(image_origin.shape)) # Print the shape of the image
cv2.imshow("image",image_origin) # Display the image
cv2.waitKey(1)
def rosShutdownHook(): # This will be called when the node exits
rospy.loginfo("VisionTest node is killed.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
rospy.init_node("VisionTest", anonymous=True) # Initialize the ROS node
rospy.on_shutdown(rosShutdownHook) # Set the callback when the node exits
chinV = Vision()
rospy.spin()The above example subscribes to the
/camera/color/image_rawtopic to obtain RGB image messages, converts ROS messages to OpenCV image format (i.e., numpy arrays) throughcv_bridge, and displays them.
Subscribing to Depth Information
Python Example
#! /usr/bin/env python
# coding=UTF-8
import rospy # ROS Python library
from cv_bridge import CvBridge, CvBridgeError # Library for converting msg data type images to OpenCV image format
from sensor_msgs.msg import Image # Message type for the topic
import cv2 # OpenCV-Python library
import numpy as np
class Vision():
def __init__(self):
self.topic_name = '/camera/aligned_depth_to_color/image_raw' # Topic name
self.__cv_bridge = CvBridge()
rospy.Subscriber(self.topic_name, Image, self.__image_callback, queue_size=1) # Define the subscriber, including topic name, message type, callback function, and queue size
def __image_callback(self, msg): # Callback function for the message, the received message is in msg
try:
image_origin = self.__cv_bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, msg.encoding) # Convert to numpy matrix format through cv_bridge
except CvBridgeError as err:
rospy.logerr(err)
return
print("depth shape is {}".format(image_origin.shape))
def rosShutdownHook(): # This will be called when the node exits
rospy.loginfo("VisionTest node is killed.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
rospy.init_node("VisionTest", anonymous=True) # Initialize the ROS node
rospy.on_shutdown(rosShutdownHook) # Set the callback when the node exits
chinV = Vision()
rospy.spin()Through the above example, you can obtain the depth image matrix aligned with the RGB image from the
/camera/aligned_depth_to_color/image_rawtopic, with a size of (height x width) = (480 x 640). After obtaining this matrix, you can extract the distance of each pixel point in the image individually, with the unit being mm (note that if the distance of some areas is 0, it indicates that the distance of the pixel point is invalid, and the minimum depth distance is approximately 0.28m).